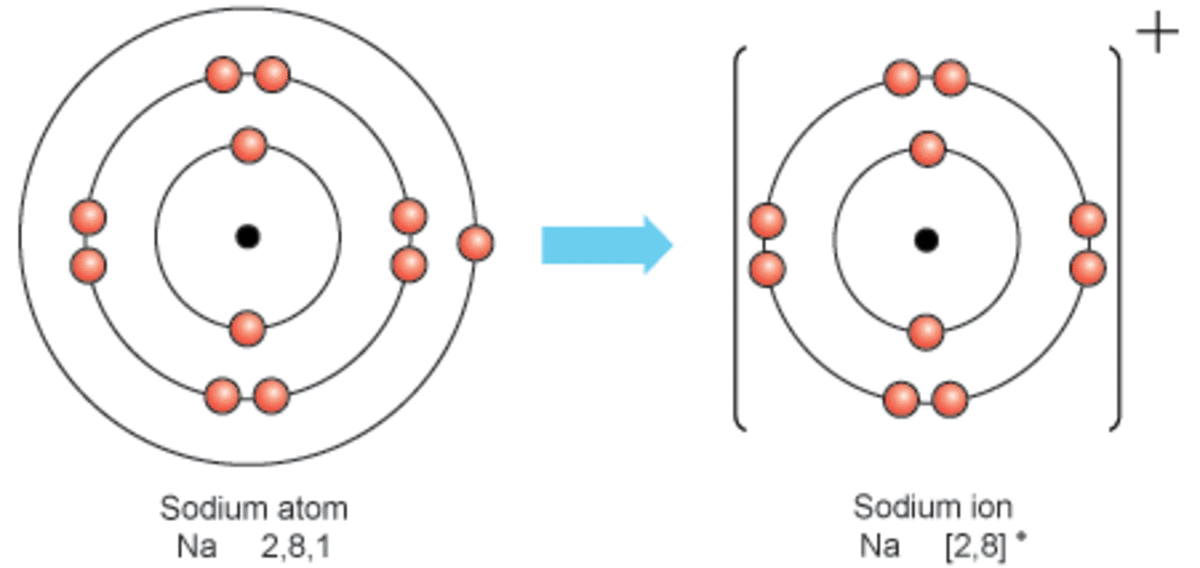
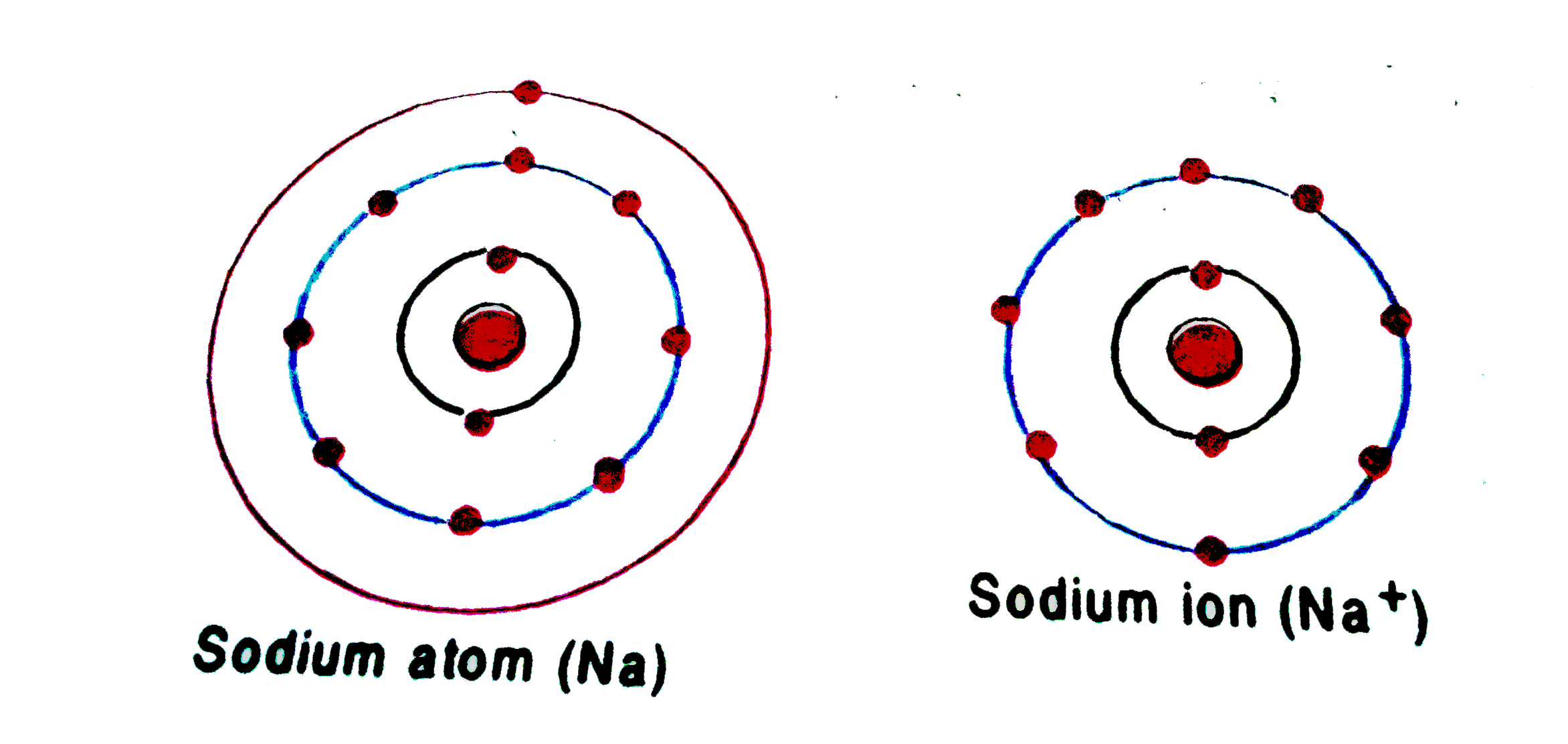
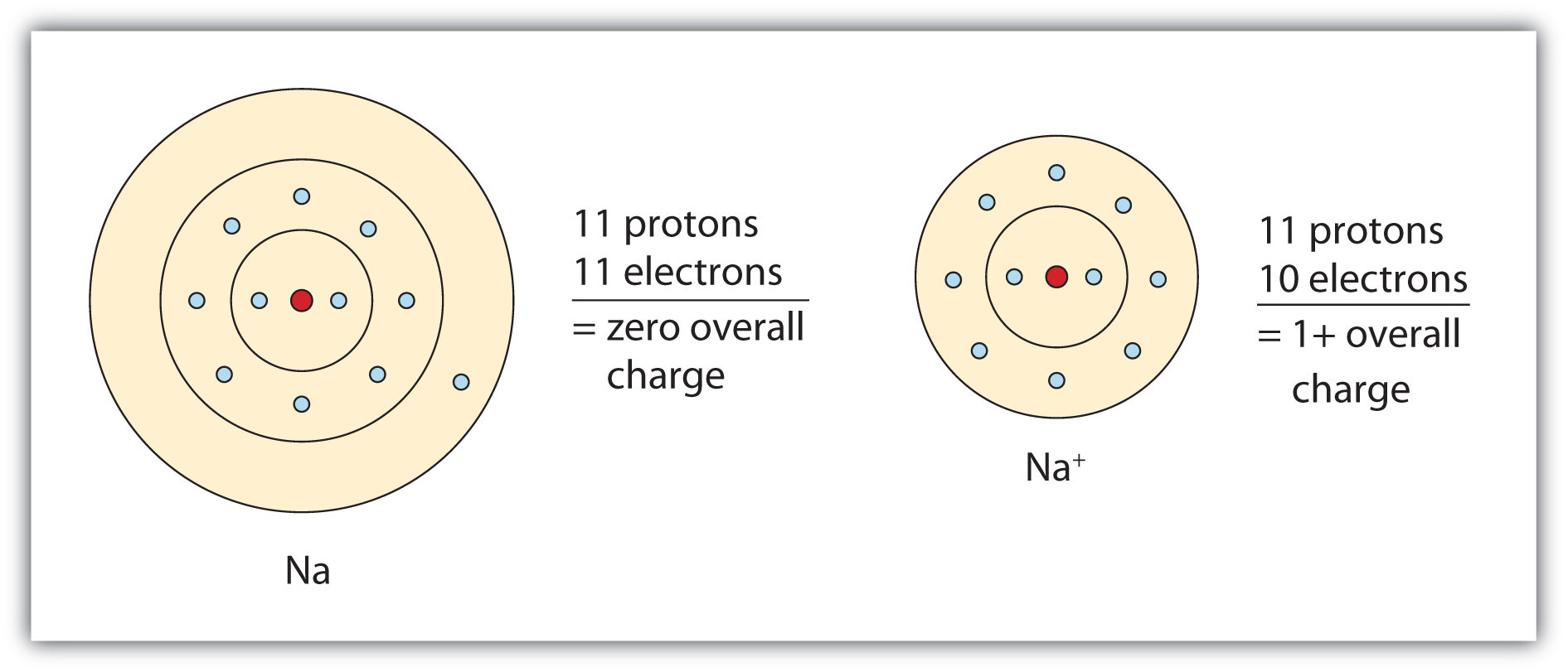
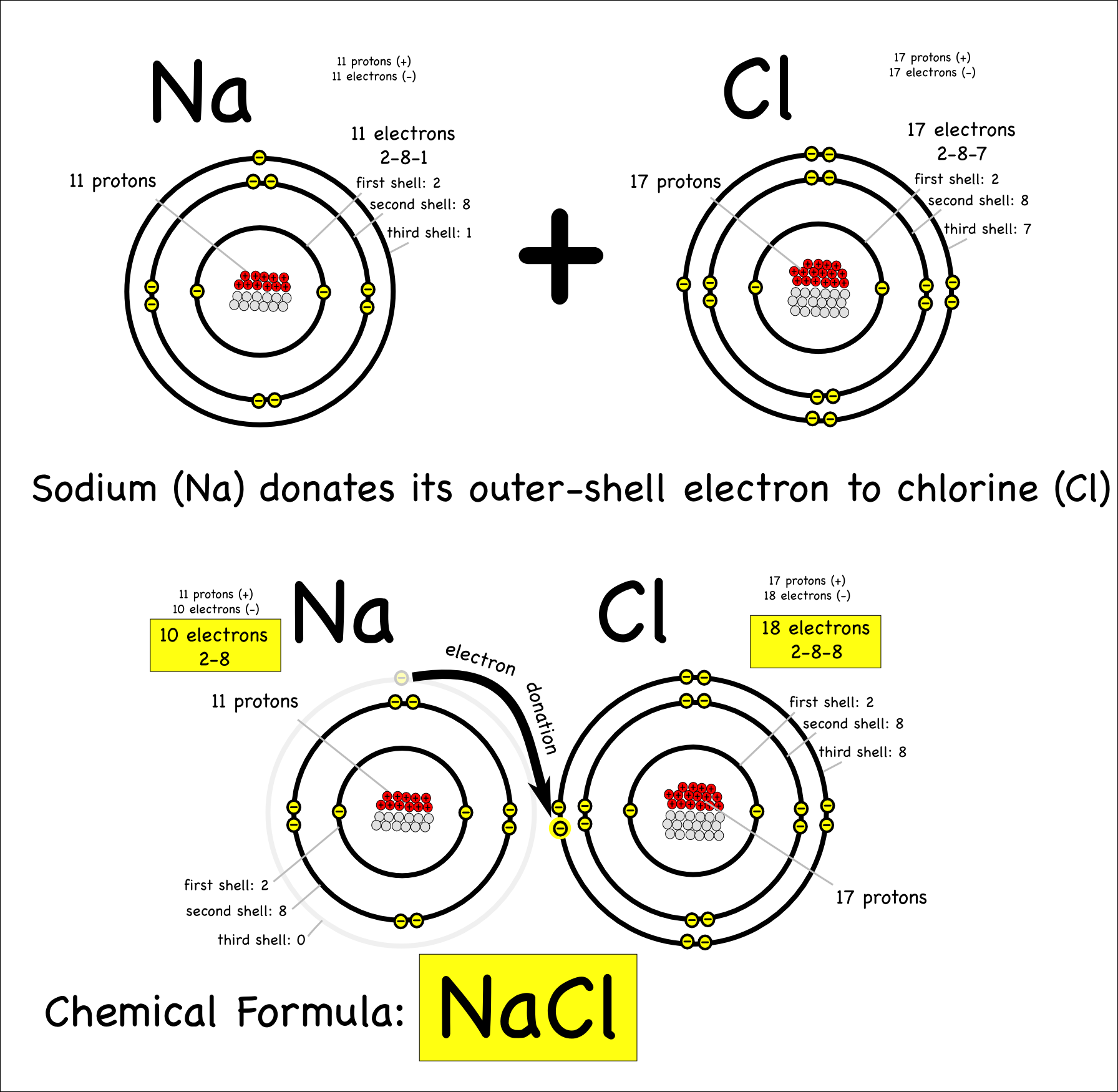
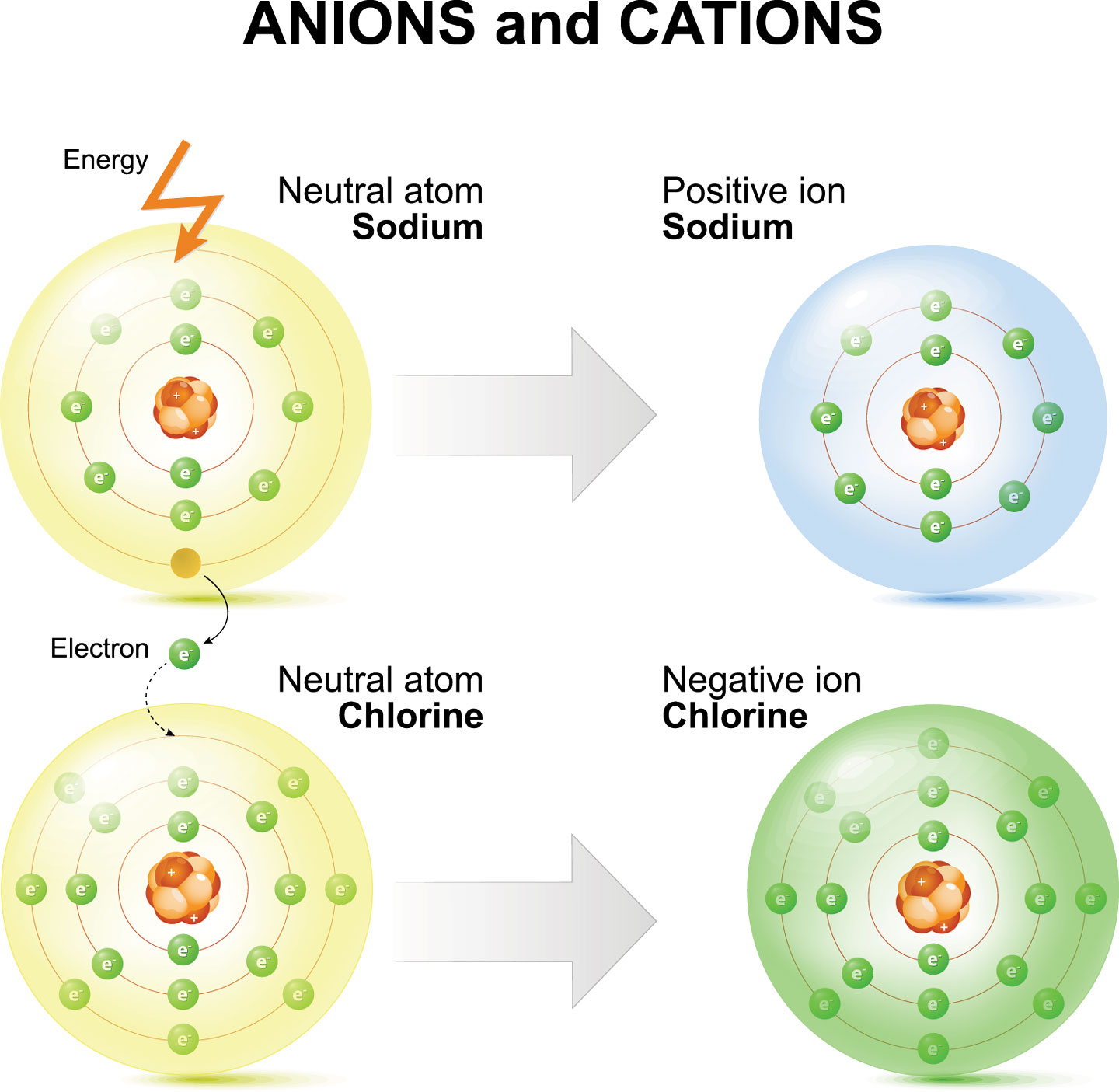
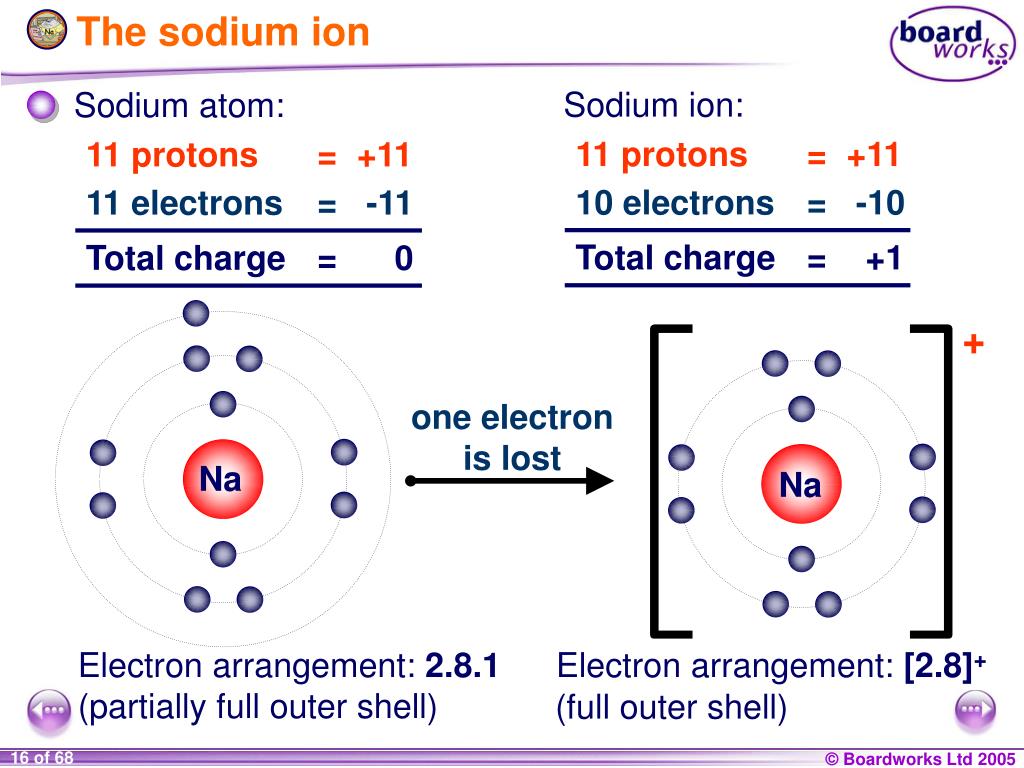
Sodium Forms An Ion With A Charge Of - Sodium metal is easily oxidized. The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion. For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium. Well, we form a na^+ ion. The sodium ion still has. When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge.
Well, we form a na^+ ion. The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion. The sodium ion still has. When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium. Sodium metal is easily oxidized.
For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium. The sodium ion still has. When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. Well, we form a na^+ ion. The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion. Sodium metal is easily oxidized.
Chemical Bonding How Do Atoms Combine? What Are the Forces That Bind
The sodium ion still has. When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. Well, we form a na^+ ion. The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion. For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium.
Sodium Electron Configuration Electron Configuration Sodium What is
The sodium ion still has. Sodium metal is easily oxidized. For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium. The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion. When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge.
Ions
For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium. When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. Well, we form a na^+ ion. The sodium ion still has. The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion.
Sodium Forms an Ion With a Charge of JasminehasGillespie
For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium. Well, we form a na^+ ion. When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. The sodium ion still has. The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion.
subatomic particles Montessori Muddle
Sodium metal is easily oxidized. The sodium ion still has. The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion. Well, we form a na^+ ion. When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge.
Explainer Ions and radicals in our world Science News for Students
The sodium ion still has. Well, we form a na^+ ion. When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. Sodium metal is easily oxidized. For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium.
Ions Types, Summary, Classification & Facts
When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium. Well, we form a na^+ ion. The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion. The sodium ion still has.
Sodium Electron Configuration (Na) with Orbital Diagram
For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium. Well, we form a na^+ ion. When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. The sodium ion still has. Sodium metal is easily oxidized.
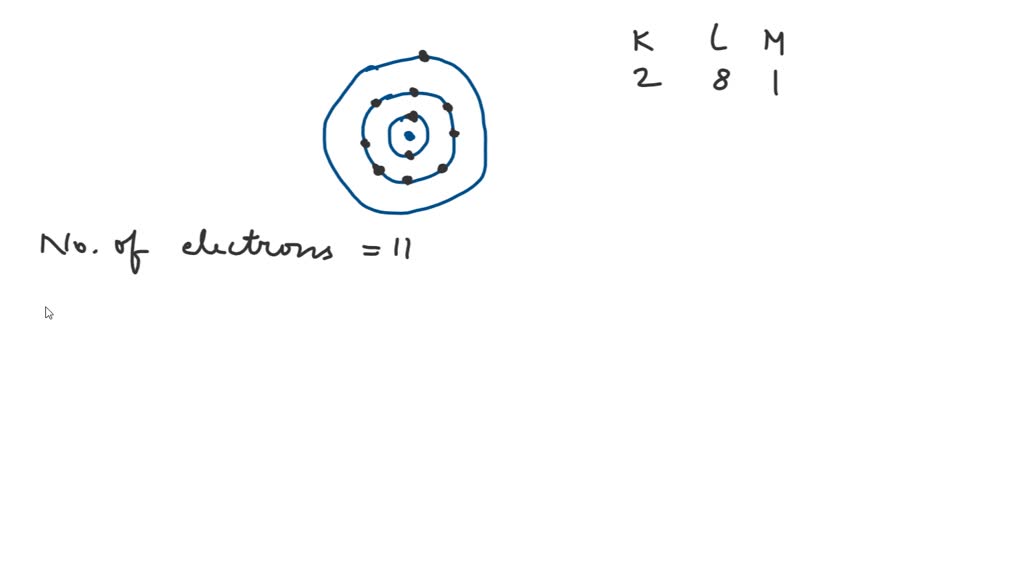
SOLVED Sodium has 11 electrons arranged in three energy levels. In
When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. Well, we form a na^+ ion. For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium. The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion. The sodium ion still has.
PPT KS4 Chemistry PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5413898
The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion. When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium. Well, we form a na^+ ion. Sodium metal is easily oxidized.
When Sodium Atoms Form Ions, They Always Form A 1+ Charge, Never A 2+ Or 3+ Or Even 1− Charge.
The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion. Well, we form a na^+ ion. Sodium metal is easily oxidized. The sodium ion still has.